작성일: 2024년 2월 21일
PPTP, L2TP 같은 터널링을 사용할 수 없는 상황에서
방화벽 건너편의 네트워크에 접속할 일이 발생하면, SSH Port Forwarding을 임시방편으로 사용하는 것도 좋다.
물론 전제 조건이 있다.
- SSH 접속할 수 있도록 방화벽 허용 규칙
또는
- DNAT Rule
또는
- 공유기의 Port Forward Rule이 미리 설정되어 있어야 한다.
즉, 원격 Network에 SSH 접속 만큼은 가능한 환경이라는 가정하에 아래 설명을 봐야 한다.
간단하게 한번 훑어보고 실습 환경으로 가보자.
SSH Tunneling에는 3가지가 있다.
- Local Port Forwarding (Local Tunneling)
- Remote Port Forwarding
- Dynamic Port Forwarding
각 Tunneling 방식에 대해서는 아래 구체적으로 설명하기로 한다.
우선 접속할 대상 Network의 SSH 서버의 설정을 수정해야 한다.
SSH Server Config 설정
$ sudo -s
$ vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
... 중간 생략 ...
AllowTcpForwarding yes # <-- yes로 변경
GatewayPorts yes # <-- yes로 변경
... 중간 생략 ...
$ systemctl restart sshd
준비 작업 끝 !
예시를 들어서, Local Tunneling에 관해서 설명해보면 이렇다.
SSH Local Port Forwarding (Local Tunneling)
아래 그림과 같이 집에 있는 내 맥북 PC에서 회사에 있는 VNC 서버에 접근해보겠다.
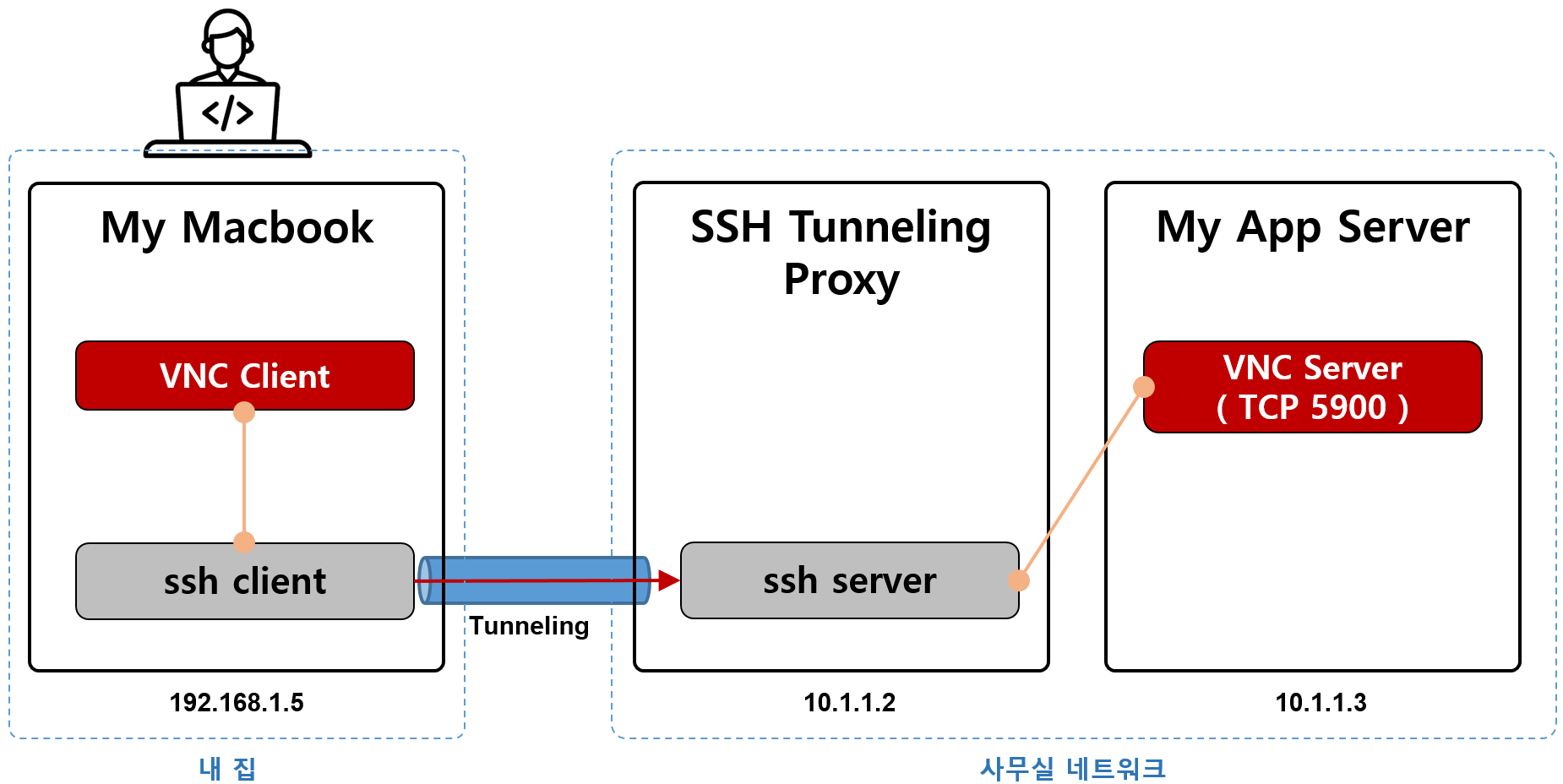
위 네트워크 구성도를 참고하여 내 PC(맥북)에서 아래의 명령을 수행한다.
(위 구성도와 아래 명령에 있는 IP Address 값을 매핑해서 보면, 아래 명령의 의미를 이해할 수 있다)
$ ssh -L 5900:10.1.1.3:5900 root@10.1.1.2
그리고 내 PC(맥북)에서 RealVNC Viewer 또는 TigerVNC Viewer에 새 연결 정보를 설정해야 하는데,
주소를 localhost (또는 127.0.0.1)으로 입력해야 한다. (아래 화면을 참고)
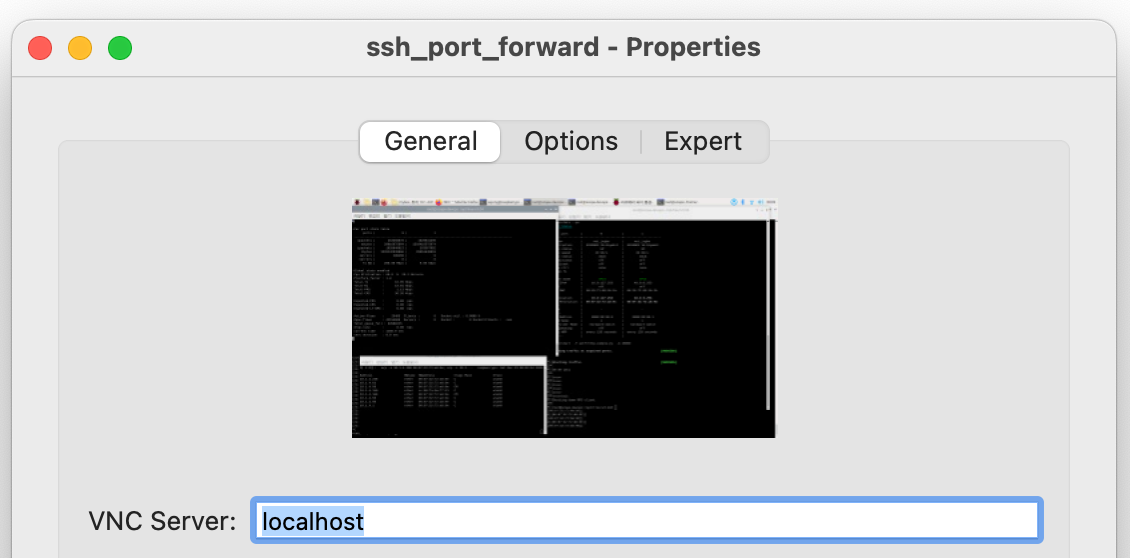
위와 같이 VNC Server의 주소를 설정하고, 접속 버튼을 누르면
VNC 접속 요청 트래픽은 아래 순서로 흘러간다.
1) 내 맥북 PC VNC Client
2) localhost의 ssh client (192.168.1.5:5900)
3) 사무실의 ssh server (10.1.1.2)
4) VNC Server (10.1.1.3:5900)
원하는 VNC 접속 성공 !!
SSH Remote Port Forwarding
이번에는 완전 반대의 경우를 생각해보자.
사무실 쪽에서 SSH 서버 접속을 허용하지 않아서 Local Tunneling이 안 되는 경우라면,
사무실에 있는 누군가(나의 친한 동료)가 내 집에 있는 내 맥북에 SSH Tunneling을 요청해주어야 한다.
물론 내 맥북이 Public network에 노출되어야 한다.
이런 방식을 Remote Tunneling이라고 한다.
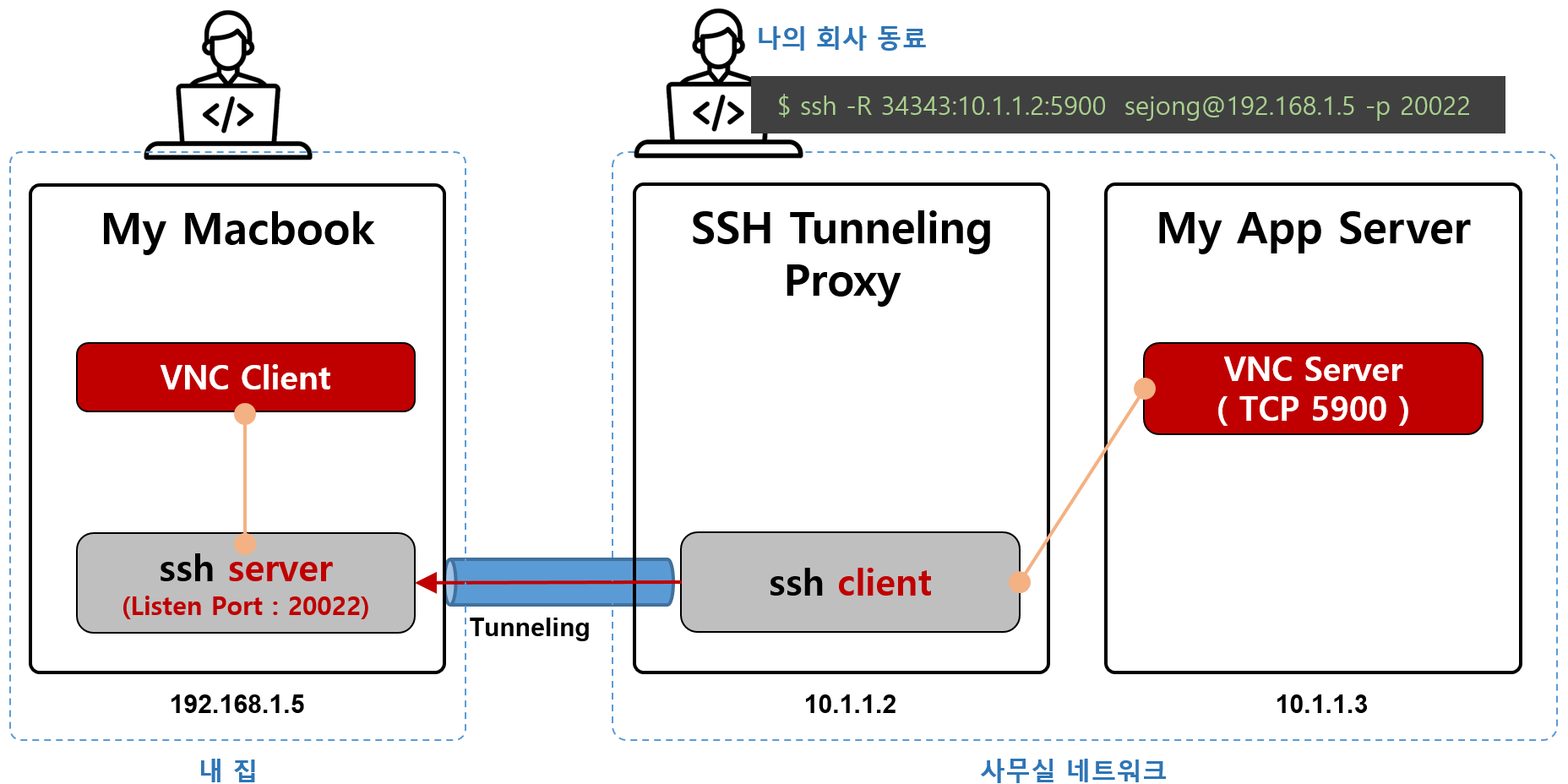
사무실에서 나의 동료가 회사 Linux 서버에서 아래와 명령을 실행해준다.
$ ssh -R 34343:10.1.1.2:5900 sejong@192.168.1.5 -p 20022
그러면 위 명령 때문에 내 맥북 PC에는 TCP Listening port 34343가 생성된다.
## 집에 있는 내 맥북 PC에서 명령을 실행한 결과
$ netstat -anp | grep LISTEN
... 중간 생략 ...
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:34343 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
... 중간 생략 ...
이제 내 맥북에서 VNC Viewer를 이용해서 아래 화면과 같이 설정하고 회사 Network로 접속해보자.
VNC Server 주소는 localhost 또는 127.0.0.1 으로 설정하면 된다.
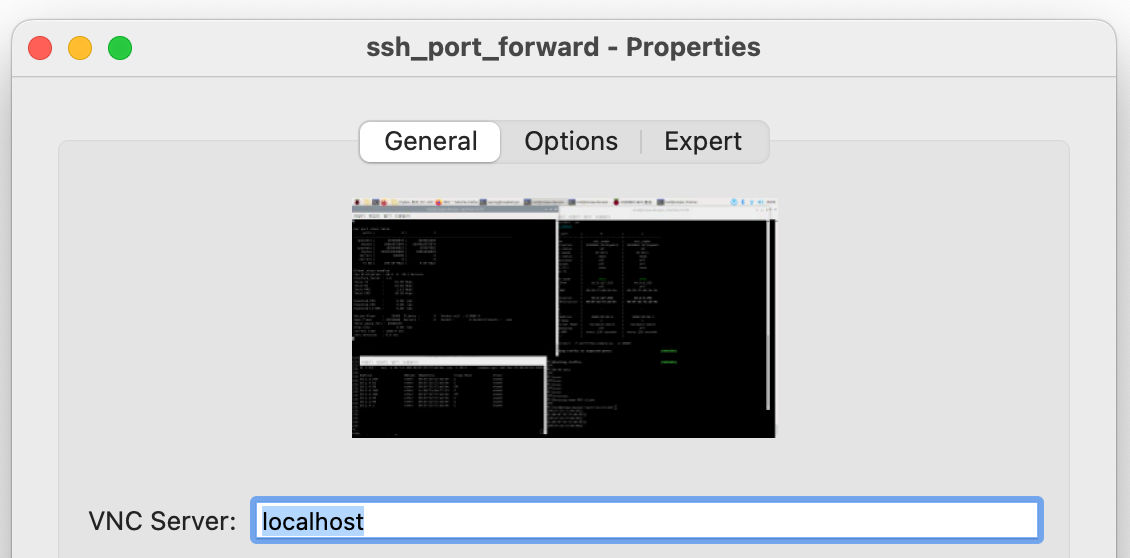
위와 같이 VNC Server의 주소를 설정하고, 접속 버튼을 누르면
VNC 접속 요청 트래픽은 아래 순서로 흘러간다.
1) 내 맥북 PC VNC Client
2) localhost의 ssh client (192.168.1.5:5900)
3) 사무실의 ssh server (10.1.1.2)
4) VNC Server (10.1.1.3:5900)
원하는 VNC 접속 성공 !!
'Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| ip link 명령으로 macvlan network interface 만들기 (0) | 2024.02.09 |
|---|---|
| WireGuard로 나만의 커스텀 VPN 서버 구축(일명, Bespoke VPN Server) (0) | 2024.01.08 |
| Juniper Switch 제어를 위한 Python Script 예제 (Junos PyEX 패키지 사용하기) (0) | 2023.12.11 |
| CISCO TRex - Network Traffic Generator (네트워크 성능 계측기), 설치 및 테스트 (0) | 2023.11.12 |
| Raw Ethernet Packet - Example Source Code (0) | 2023.10.06 |